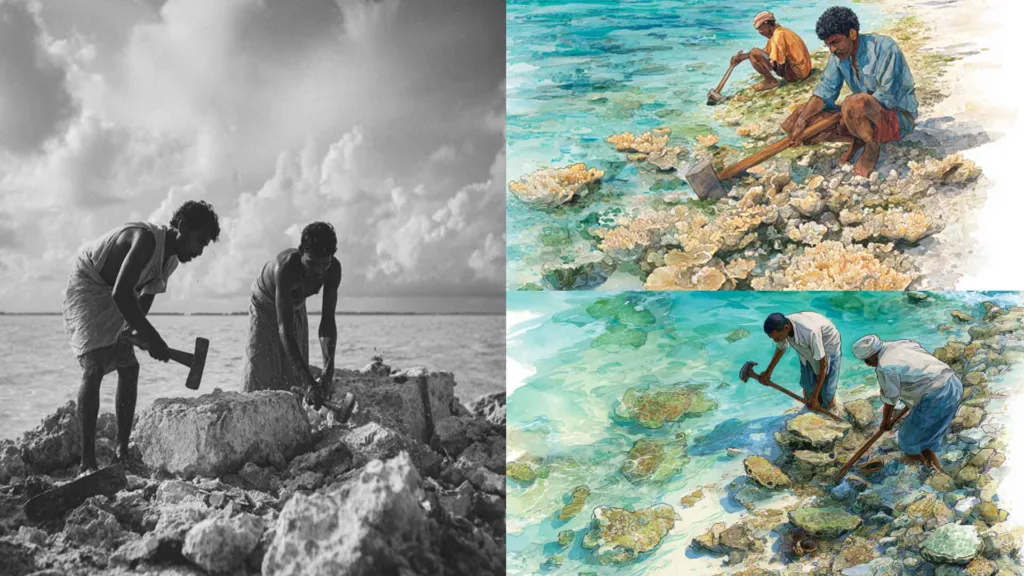
Apart from the rich biodiversity of the Maldivian ocean, mangroves are also part of the ecosystem rich in biodiversity. Fourteen mangrove species are found in Maldives (A. Shazra, S. Rasheed and A.A. Ansari, 2008). Maldivian islands are geographically isolated and the mangrove systems found in the islands are also different.
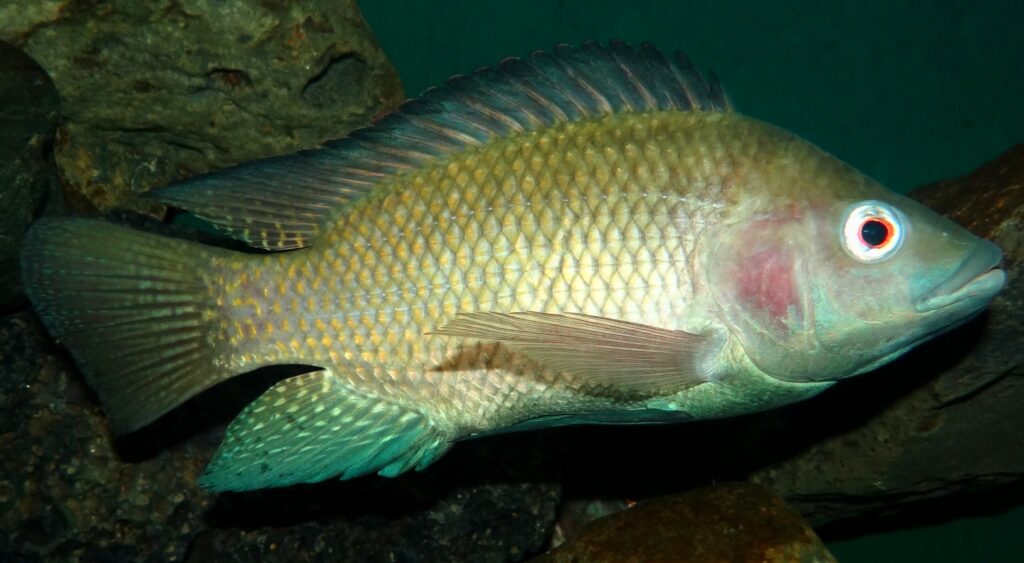
There are around 80 islands with mangroves and wetlands. They are abundant with wildlife and plant species. These wetlands are home to many types of fauna. In this article, I am writing about the most common freshwater fish found in the lakes in the mangroves of Maldives. Footumaha or Tilapia is the most abundant species of fish in the two freshwater lakes of Fuvahmulah as well. People on our island normally do not eat this fish although some people eat this delicious fish.
I remember my father catching tilapia from the lake (Dhadimagi kilhi) of our district way back in the late 80s and kept the fish in a large cement tank in the backyard of our household. My mom fried the fish and we ate. It has a mild taste. It was delicious. It is sweet and flaky. Tilapia might be the fish that we love to hate. But there can be a lot to love. This great fish can live in fresh or saltwater. It is the second-most popular farmed fish on the planet, says Kevin Fitzsimmons, PhD, tilapia researcher and professor in the Department of Soil, Water and Environmental Science at the University of Arizona. “It can be used in virtually any fish recipe,” he says.
Tilapia can easily be harvested. Some of these species adapt very well to the sea. It is the second most farmed fish in the world after Carp fish. There are three main Tilapia species: Nile (black) tilapia, Mozambique (or red) tilapia and blue tilapia. In ancient times, for example in Egypt, it was farmed. Now it has been farmed in more than 85 countries in the world. In the United States, it is a very popular fish.Tilapia is a healthy source of protein. It gives vitamin D and healthy fats. It may lower cancer risk, and may protect heart health (Begum, 2024).